A new review in Space Science Reviews, highlights advances in forecasting Solar Energetic Particles (SEPs). The study outlines two main approaches: empirical models, based on past events, and physics-based models, which simulate particle acceleration and transport. It also shows how artificial intelligence and machine learning, are being increasingly used to combine multiple inputs (solar flare class, CME speed, magnetic connectivity, radio bursts, seed particle populations etc.) for better predictions. The paper also shows that observations from multiple spacecraft (e.g. Solar Orbiter, Parker Solar Probe, STEREO) are key: they help understand how SEPs propagate and how prediction accuracy depends on where you observe from. The review highlights also the challenges that the scientific community needs to face and underlines the fact that for upcoming crewed missions to the Moon, Mars, or deep space, reliable SEP forecasting isn’t optional — it is safety-critical, as better predictions can protect satellites, power grids, aviation, and astronauts, while advancing these models ultimately strengthens our resilience to space weather.
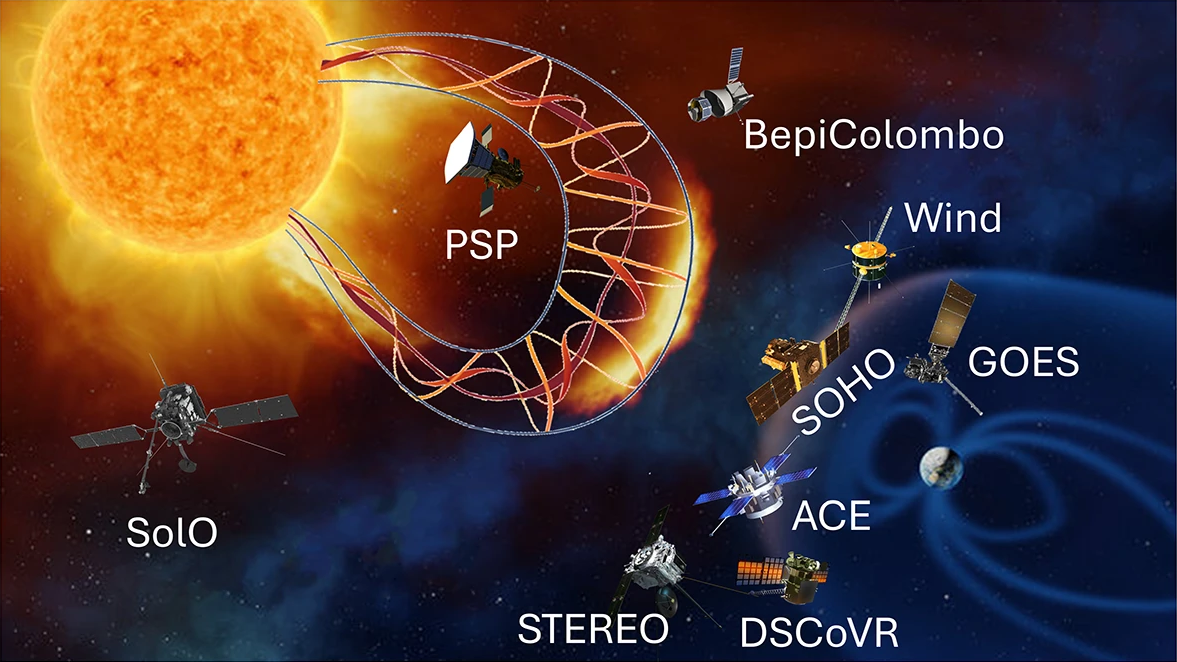
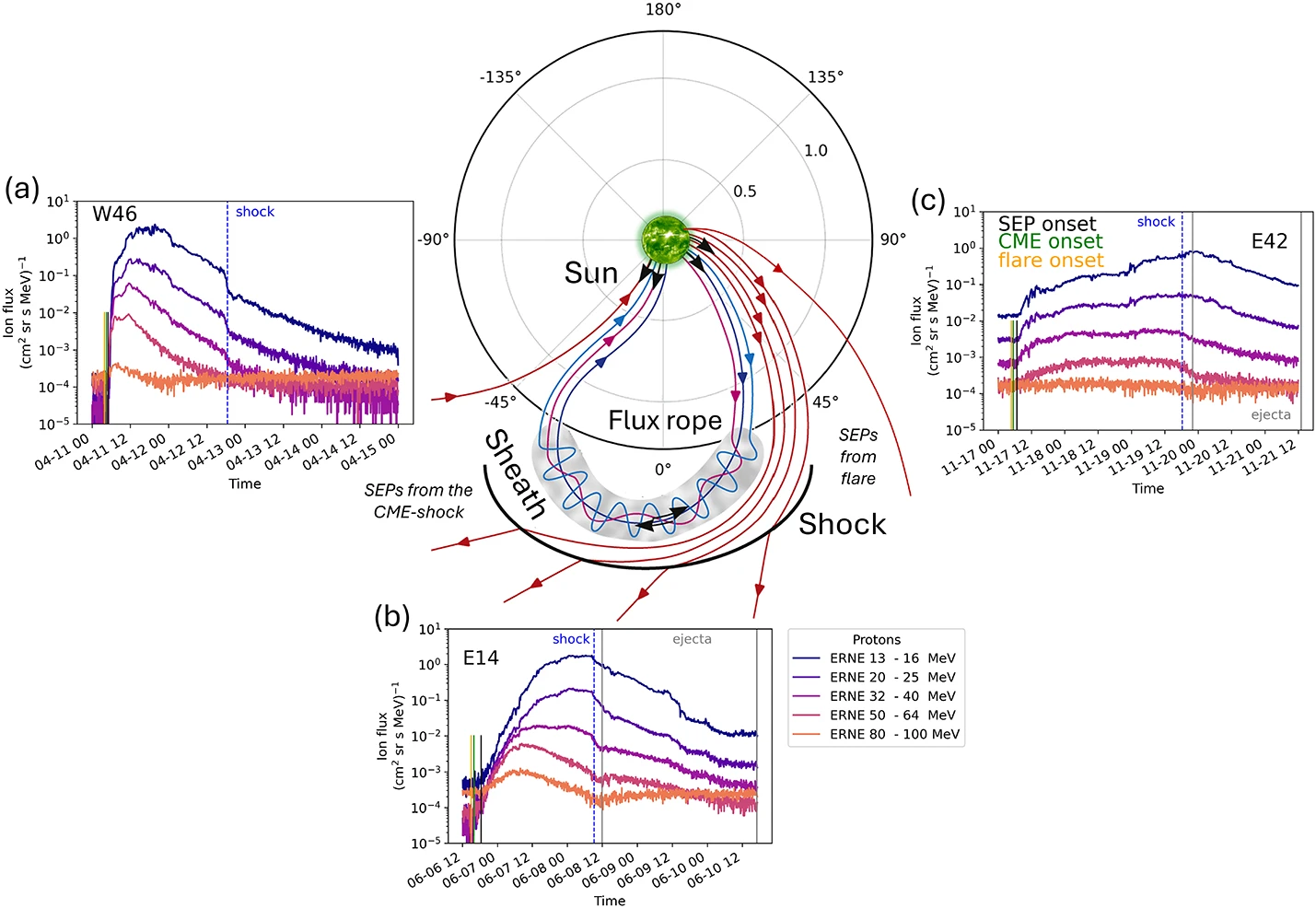
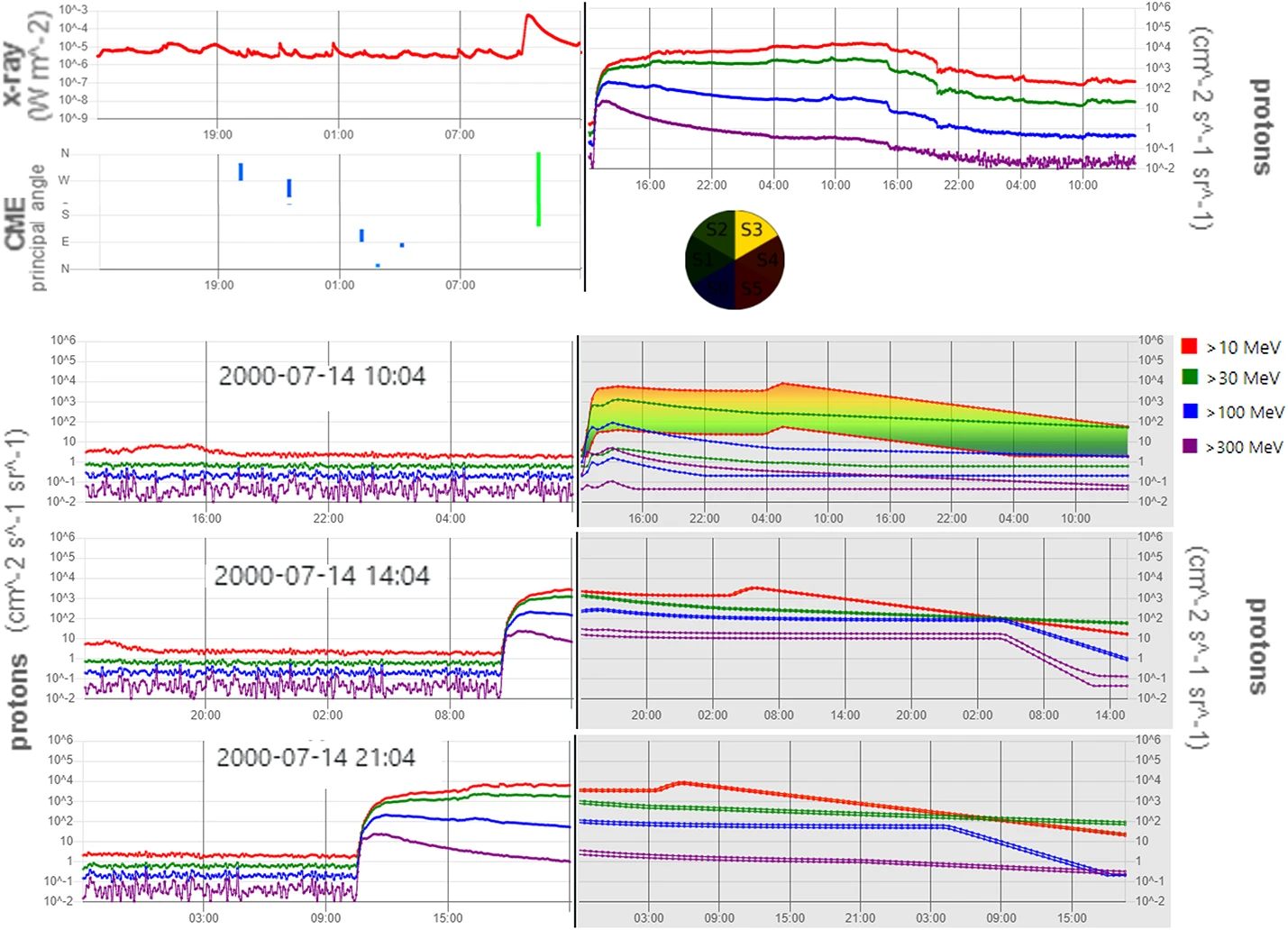
These findings directly support SPEARHEAD’s mission to strengthen Europe’s resilience against space weather, protecting critical technologies.
More info: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11214-025-01211-4


